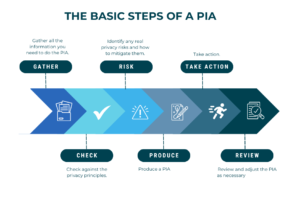
A Privacy Impact Assessment, or PIA, is a process used to determine how a program or activity could affect the personal privacy of individuals. Risk management and legal compliance are key goals of a PIA. Generally, PIAs generate a final report which describes how technology works, how information is collected, where it travels and is stored, risk factors, and mitigation strategies.
In Canada, federal public institutions are often required to conduct PIAs when implementing a system that collects personal information. The Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat has enforced a Directive on Privacy Impact Assessment which applies to any department or ministry of state of the Government of Canada, any parent Crown corporation, and any wholly-owned subsidiary of such a corporation. In addition to requiring that PIAs be conducted, the Directive requires that certain sections of a PIA be made publicly available. The Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada also has federal jurisdiction and hosts a PIA webpage.
In British Columbia, Section 69 (5) of the Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy Act (FOIPPA) requires public bodies to conduct a PIA. The provincial government hosts a PIA webpage with guidance.
Similar PIA requirements are in place in Canadian provinces including Alberta, Saskatchewan, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Ontario.
PIA Steps image source: https://privacy.org.nz/publications/guidance-resources/privacy-impact-assessment-toolkit/